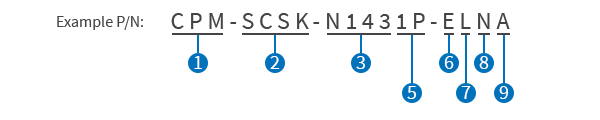-
Products
- ClearPath All-In-One Servo Motors ClearCore I/O & Motion Controller ClearLink EtherNet/IP Motion & I/O Controller IPC DC Power Supplies Hudson BLDC Servo Motors Meridian Integrated Controllers Eclipse Digital Servo Drives Motor Brakes Planetary Gearboxes Legacy ProductsClearPath All-in-One Servo Motors
 ClearPath integrates all servo components into one compact package:
ClearPath integrates all servo components into one compact package:- Motion controller
- Brushless, permanent magnet motor
- High-resolution encoder
- Digital servo drive electronics
- 3-year warranty
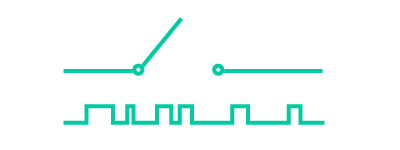
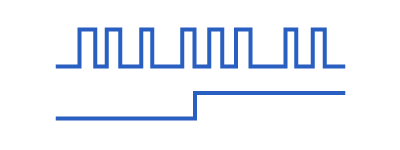
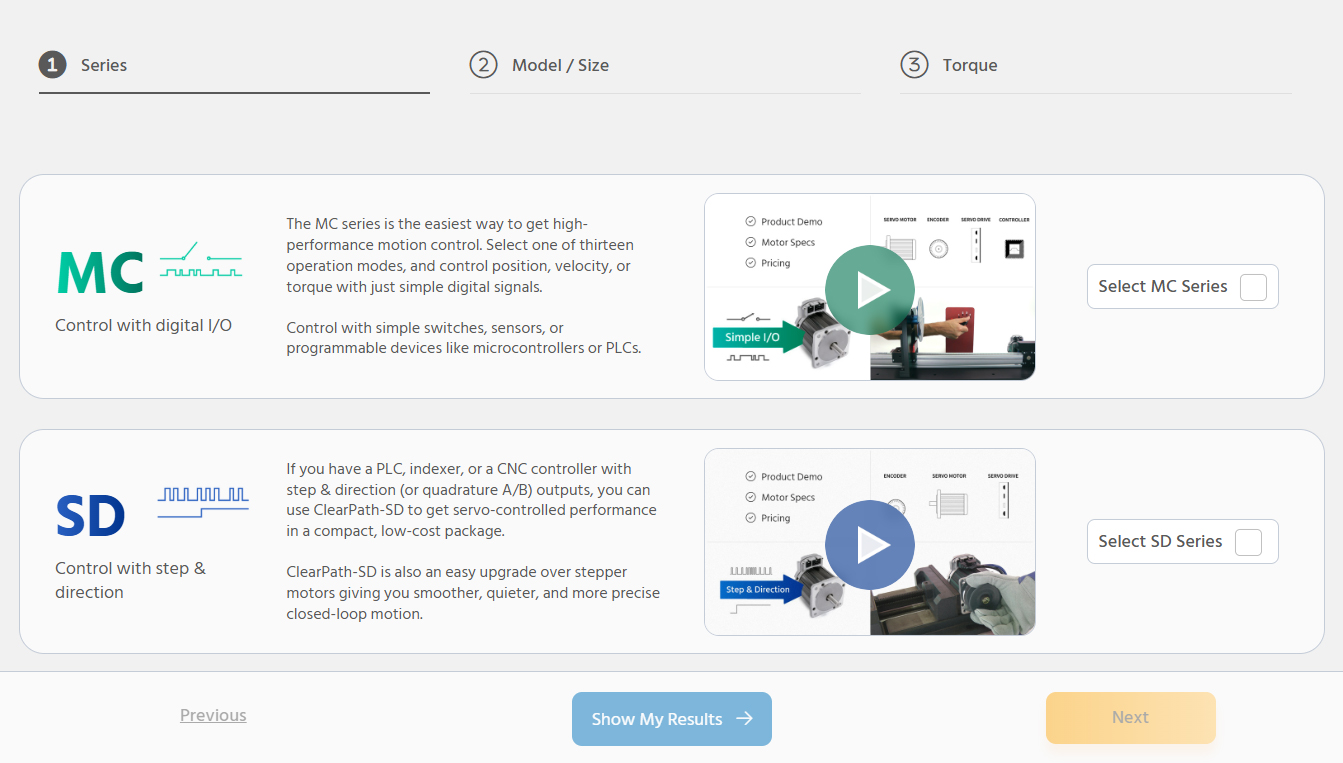
Choose a Motor Control SeriesClearPath Motor Selection GuideIf you need help selecting the right ClearPath motor, use this guide to narrow your options in 3 easy steps.- Choose your series, model, and power range
- Get a list of relevant specs and pricing
- Compare ClearPath models side-by-side
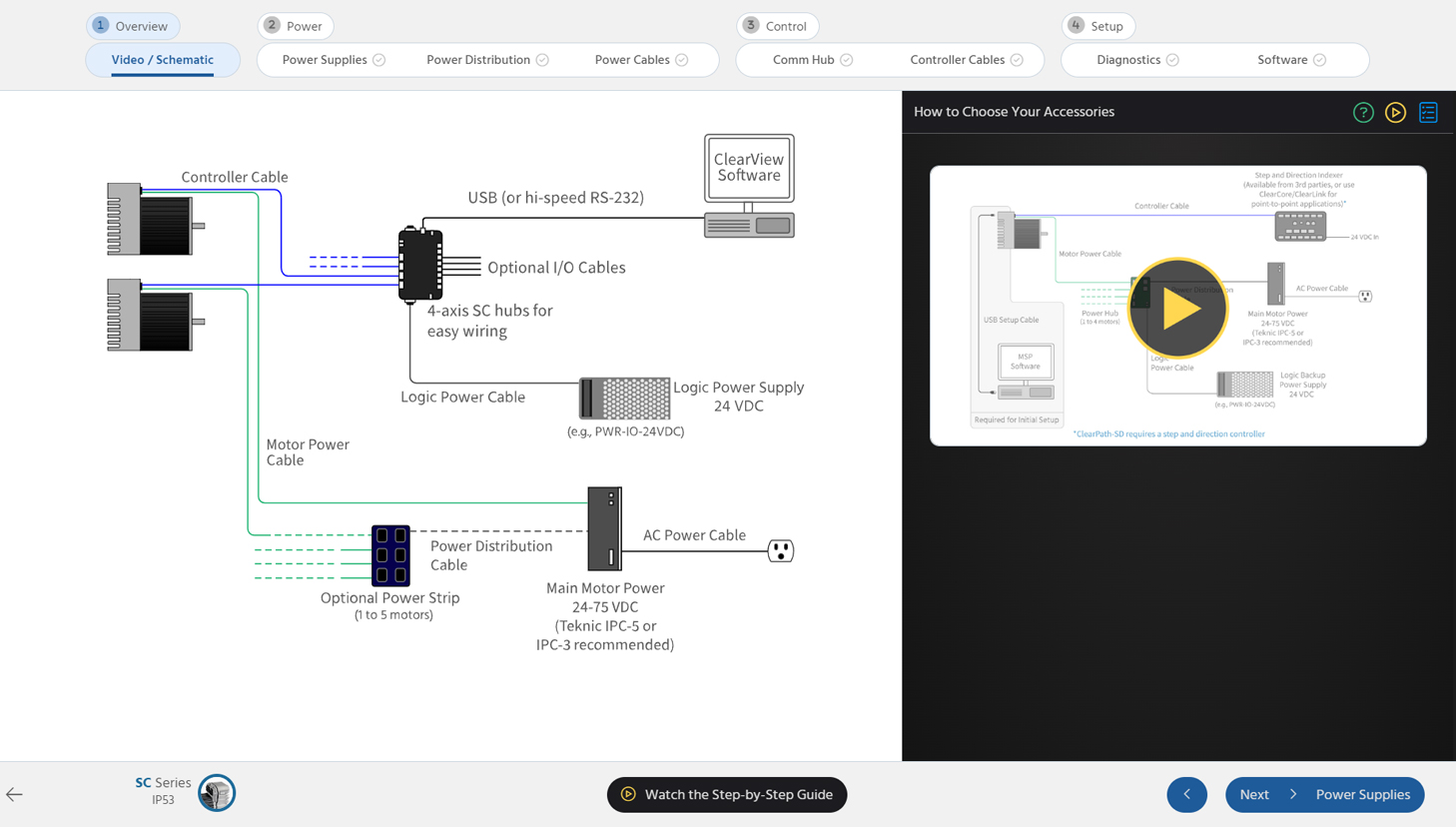
ClearPath Accessories GuideFor help with selecting accessories for your specific ClearPath system, use this walkthrough.- Step-by-step guide to select recommended and optional accessories
- Comprehensive overview video for each accessory
- Use the interactive accessories schematics to easily purchase the parts you need
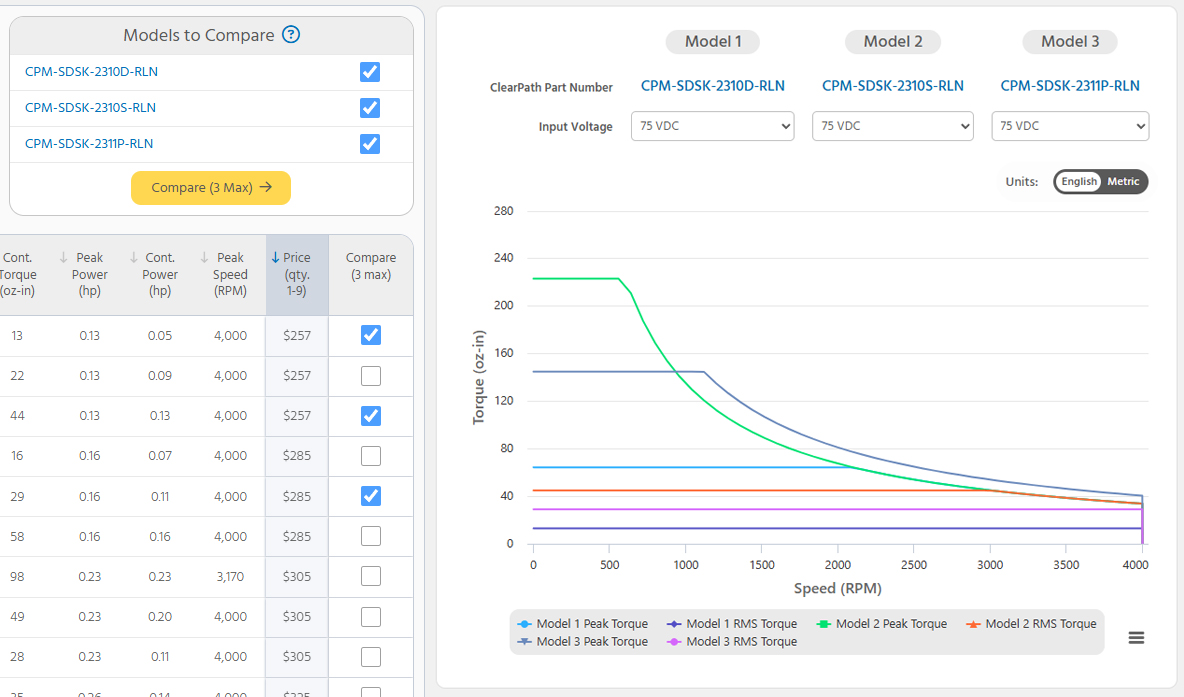
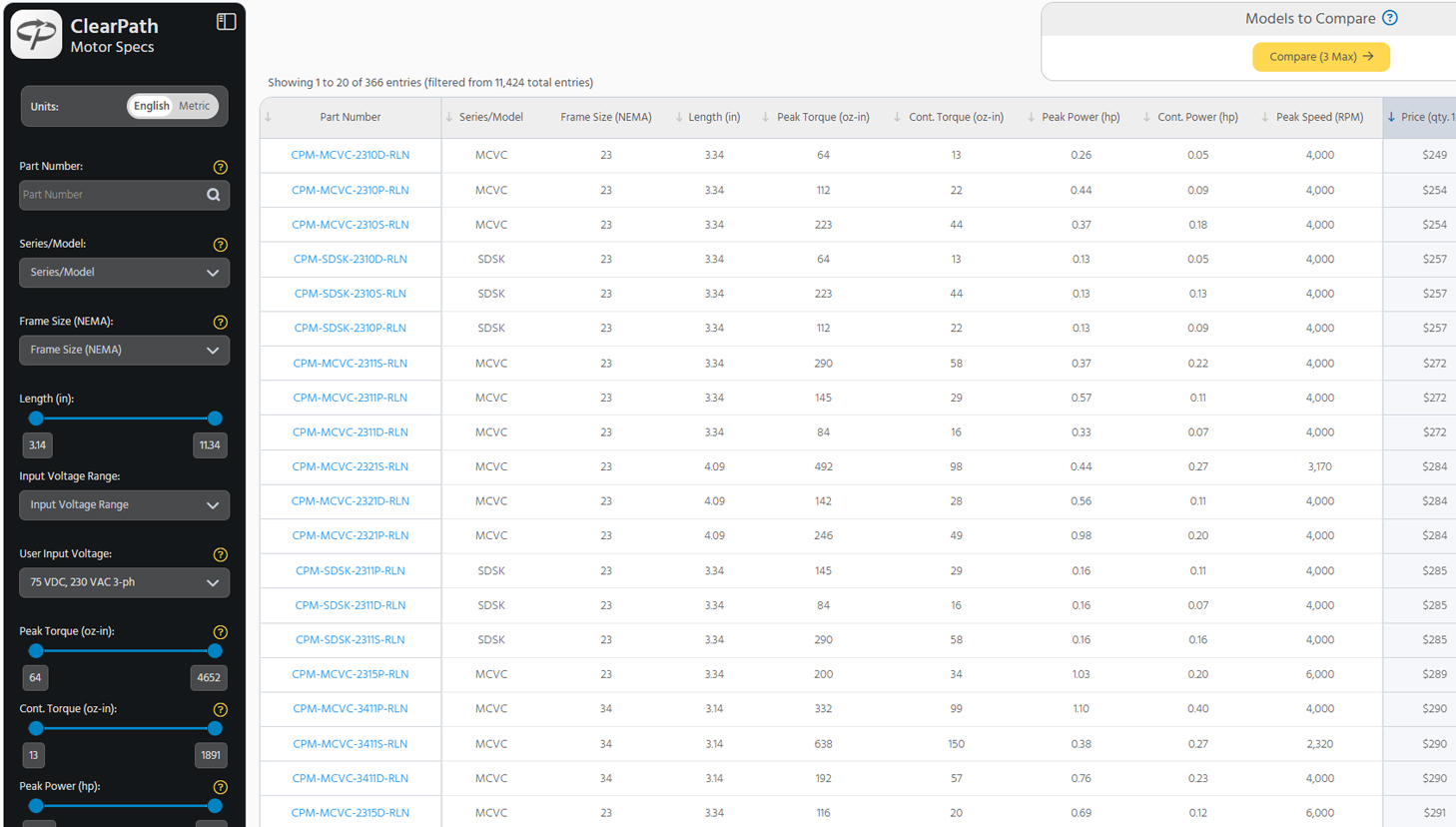
ClearPath Motor Specs & PricingFor engineers that already know their ClearPath series and exact requirements:- See specs and pricing for 1000+ part numbers
- Filter by torque, speed, power, voltage, frame size, length, and more
- Overlay torque vs. speed curves and compare specs and pricing
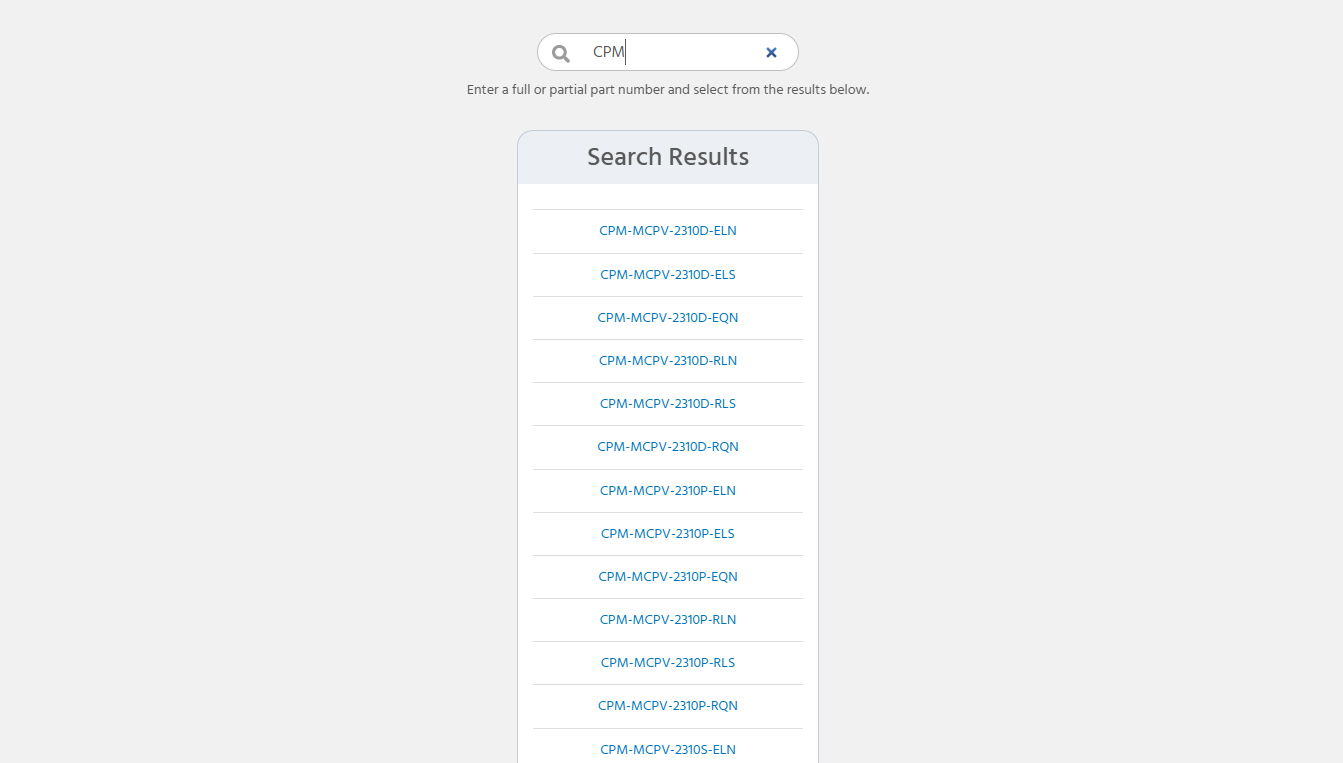
ClearPath Part Number Index/SearchIf you already know your part number(s), use the index to quickly find:- Pricing and ordering of ClearPath motors or accessories
- Specifications (including torque vs. speed curves)
- Drawings, manuals, or setup software
Control ClearPath servos with your EtherNet/IP PLC
using a ClearLink controllerHudson BLDC Servo MotorsTeknic's Hudson servo motors are designed to excel in the most demanding OEM applications.- Reduce motor footprint and maximize power output with optimized magnet shape, motor skew, and rotor geometry
- Improve machine reliability with a brushless servo motor designed with oversized bearings and class H windings
- Increase machine performance with Hudson's high torque density and fast electrical time constant
- Buy online, starting at $214
- 3-year warranty
Meridian Integrated ControllersMeridian is an integrated motion controller and digital servo drive that is capable of controlling servos, linear motors, and steppers.- Reduce machine vibration and increase throughput with g-Stop™ anti-resonance
- Use the Accelerated Prototyping System™ to diagnose performance issues and reduce development time
- Improve stepper motor smoothness and increase power output with vector sinewave commutation
- Get up and running quickly with the sFoundation source code library
- 3-year warranty
Eclipse Digital Servo DrivesEclipse is a state-of-the-art digital brushless servo drive capable of controlling brushed and brushless servo motors.- RAS motion smoothing algorithm reduces move and settling time, noise, and mechanical wear
- Teknic's proprietary servo algorithms eliminate overshoot and improve machine performance
- Quickset digital oscilloscope and move generator reduce development time
- 3-year warranty
Motor BrakesSpring applied power-off (or fail-safe) brakes are used in applications that require the axis to stay in position, even if the machine loses power or is turned off. Brakes are a great option for vertical applications or when additional safety measures are required.- Front mount compatible with any NEMA 23 or NEMA 34 motor frames
- 24 VDC input for easy actuation
- NEMA 23 brakes start at $245
- NEMA 34 brakes start at $327
- Buy Online; 90-day satisfaction guarantee
- 3-year warranty
Planetary GearboxesTeknic's planetary gearboxes are an effective solution to dramatically increase the torque output of a motor, among other key benefits.- Compatible with any NEMA 17, 23, 34, 56 or 143 motor
- Increase motor load handling
- Offloads motor bearings, allowing for increased axial/radial loading
- Compact design is ideal for space-constrained applications
- Buy Online; 90-day satisfaction guarantee
IPC DC Power SuppliesThe Amazon™ Intelligent Power Center (IPC) is designed and built specifically for motion control applications.- High output capacitance and built-in regen control system prevents over-voltage shutdowns and the need for external regeneration control and load resistor
- High peak power drastically reduces power supply droop during motor acceleration
- Buy online, starting at $202
- Built in the USA; 3-year warranty
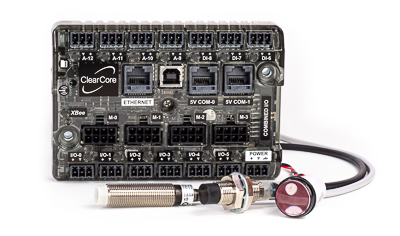
ClearCore I/O and Motion ControllersClearCore is a controller platform for industrial I/O and motion control.- Control 4 steppers or digital servos like ClearPath
- Analog/digital inputs and outputs; 24V industrial quality
- Rich C++ library with dozens of example programs
- Ethernet and serial communication
- Buy online; 90-day satisfaction guarantee; 3-year warranty
ClearLink EtherNet/IP Motion and I/O ControllerClearLink is an industrial I/O and motion controller, compatible with any EtherNet/IP scanner.- Control 4 steppers or digital servos like ClearPath
- Configurable analog/digital inputs and outputs; 24V industrial quality
- Rich EDS file support reduces development time
- Add up to an additional 64 digital I/O points
- Buy online; 90-day satisfaction guarantee; 3-year warranty
Teknic Legacy ProductsTeknic continues to advance the state-of-the-art in servo motion control. As a result, new products are engineered to provide greater performance, reliability, and value. Products that are eventually displaced by the introduction of new technology are not simply discontinued—the components continue to be manufactured and supported for as long as parts are reasonably available.When products are forced into end of life, Teknic's factory engineers work with customers who desire to extend the life of their legacy machines with newer servo components. Some of Teknic's legacy products were available for nearly 30 years before they moved to end of life status.
-
Support
-
ClearPath Start Guide
Resources to get you up and running -
ClearPath Troubleshooting
Solve common problems quickly -
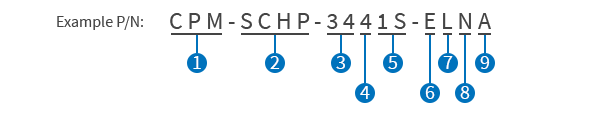
ClearPath Part Number Key
Detailed breakdown for all models -
Videos & Articles
Detailed technical guides for products and software -
FAQs
Answers to your product and policy questions -
International FAQs
Common questions for our non-US customers
-
ClearPath Start Guide
- Downloads
- About























 Show all option variants
Show all option variants Show all option variants
Show all option variants